
Introduction: The Shift from Monoliths to Micro-Frontends
The landscape of web development has been evolving rapidly. From static pages to dynamic single-page applications (SPAs), businesses are now entering an era that demands faster releases, scalable frontends, and modular architecture. While microservices revolutionized backend scalability, the frontend world faced similar challenges. That’s where Micro-Frontends come into play — an architecture that breaks down large, complex user interfaces into smaller, manageable, and independently deployable parts.
For enterprises using ASP.NET Core, Micro-Frontends offer a practical solution for integrating diverse teams, technologies, and deployment pipelines — all while maintaining performance and consistency across the application.
In this article, we’ll explore how ASP.NET Core fits perfectly into the Micro-Frontend architecture, why it’s transforming custom software development, and how businesses can implement it effectively.
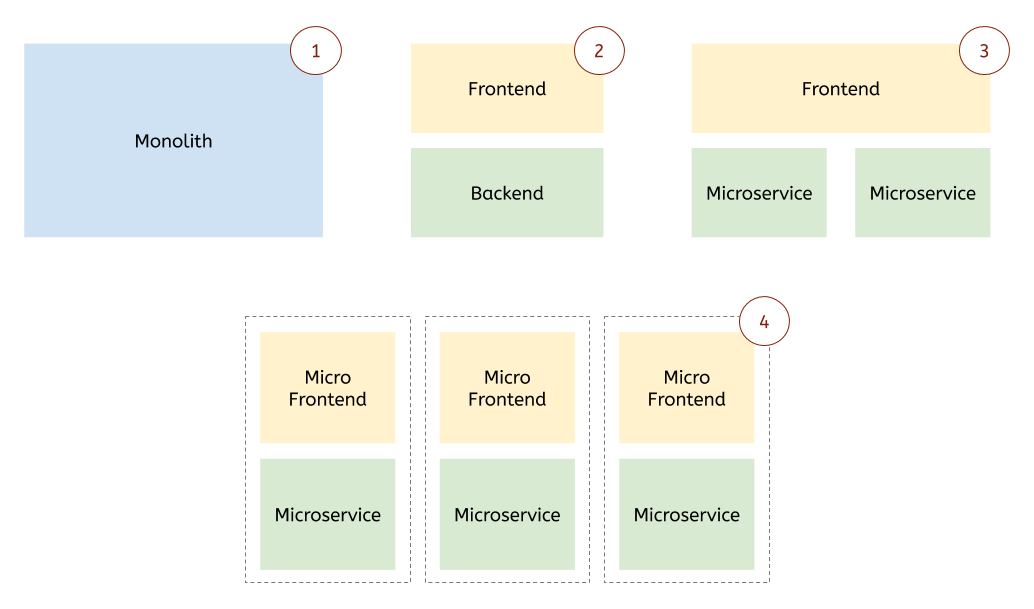
What Are Micro-Frontends?
Micro-Frontends extend the microservices concept to the frontend. Instead of having a single monolithic UI managed by one team, you can divide your application into smaller frontends — each owned by a different team, built with different technologies, and deployed independently.
Each Micro-Frontend is:
Autonomous: Teams can choose their framework (React, Angular, Vue, Blazor, etc.)
Isolated: Runs independently but communicates seamlessly with others.
Deployable: Can be built, tested, and deployed without affecting the rest of the app.
Composable: Integrated dynamically at runtime, often through container apps built in ASP.NET Core.
This modular approach boosts agility, reduces deployment risks, and accelerates enterprise web development cycles.
Why ASP.NET Core is Ideal for Micro-Frontends
1. Unified Backend Integration
ASP.NET Core offers robust APIs, middleware, and hosting flexibility — allowing backend teams to serve multiple frontends efficiently. You can design a gateway layer that routes requests to the right frontend or backend microservice.
2. Seamless API Management
ASP.NET Core integrates easily with REST and gRPC APIs, helping multiple frontend teams share consistent data sources. Combined with Azure API Management, it ensures secure, scalable access for distributed teams.
3. Cross-Platform Support
Since ASP.NET Core runs on Windows, Linux, and macOS, development and deployment pipelines for micro-frontends become more versatile and cost-effective — especially in Azure cloud application development environments.
4. Security Built-In
ASP.NET Core’s middleware, identity providers, and OAuth/JWT authentication make it easy to enforce unified security policies across multiple frontends.
5. Performance Optimization
Micro-frontends introduce multiple assets; however, ASP.NET Core’s built-in caching, bundling, and static file middleware ensure that performance remains top-tier.
Building Micro-Frontends with ASP.NET Core
Step 1: Define the Shell (Container App)
The shell app (or host app) serves as the entry point — built using ASP.NET Core. It defines routing, layout, and common UI components like headers, navigation, and footers.
Example:
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
The shell app dynamically loads different Micro-Frontends via URLs, JavaScript modules, or microservice endpoints.
Step 2: Integrate with Frontend Frameworks
Each Micro-Frontend (e.g., built with Angular, React, or Blazor WebAssembly) is served independently, often as a static web app or Razor Class Library hosted on Azure Blob Storage or CDN.
ASP.NET Core acts as a reverse proxy to route users to the correct Micro-Frontend:
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapFallbackToFile("/app1/{*path}", "app1/index.html");
endpoints.MapFallbackToFile("/app2/{*path}", "app2/index.html");
});
Step 3: Manage Shared State and Authentication
A common challenge is maintaining a shared login session or user state across micro-frontends.
Use ASP.NET Core Identity or OpenID Connect for centralized authentication. Tokens (JWT or cookies) can be shared securely between modules.
Step 4: Deploy on Azure for Scalability
With Azure cloud application development, each Micro-Frontend can be:
Hosted as an Azure Web App
Connected via Azure Front Door or Application Gateway
Managed under Azure DevOps pipelines for CI/CD
This ensures high availability, global reach, and secure operations.
Benefits of Micro-Frontends in Enterprise Development
Team Autonomy: Each team owns its deployment cycle, enabling parallel development.
Scalability: Easier to scale parts of the app based on demand.
Reduced Risk: Updates in one module won’t break the entire app.
Technology Freedom: Teams can migrate to new frameworks without impacting others.
Continuous Delivery: Independent releases make DevOps faster and more efficient.
Challenges and Best Practices
Challenges
Performance Overhead: Multiple bundles can increase load times.
Integration Complexity: Communication between frontends must be carefully designed.
Consistent UI/UX: Maintaining uniformity across modules is essential.
Best Practices
Use a Design System shared across all micro-frontends.
Implement lazy loading and CDN for faster delivery.
Use Azure DevOps for version control and CI/CD automation.
Monitor with Application Insights for real-time performance tracking.
Real-World Use Cases
E-Commerce Platforms:
Different teams handle checkout, product listings, and user accounts — all integrated under one container app.Enterprise Dashboards:
Modular dashboards built in React, Angular, and Blazor, managed under ASP.NET Core APIs.SaaS Platforms:
Feature-level deployments allow fast experimentation without risking downtime.
ASP.NET Core and the Future of Frontend Architecture
The synergy between ASP.NET Core and Micro-Frontend architecture represents the next step in scalable, enterprise-grade web development.
As organizations continue to modernize, custom software development companies are increasingly using this pattern to:
Simplify large-scale frontend management
Reduce time to market
Enable agile collaboration between distributed teams
When combined with Azure cloud application development, the potential multiplies — offering high scalability, global delivery, and unified monitoring.
Conclusion:
Micro-Frontends aren’t just a technical trend — they’re a business enabler. For enterprises looking to evolve from legacy systems into agile, scalable architectures, ASP.NET Core provides the perfect foundation.
By embracing Micro-Frontend architecture, businesses unlock faster innovation, improved maintainability, and superior user experiences — transforming traditional web apps into future-ready enterprise ecosystems.
FAQs
1. What is the main advantage of Micro-Frontends in ASP.NET Core?
They enable modular development, allowing independent deployment and maintenance of different UI modules while maintaining backend consistency.
2. Can Micro-Frontends be used with Blazor in ASP.NET Core?
Yes, Blazor WebAssembly or Server can function as individual Micro-Frontends within a shared container app.
3. How does Azure support Micro-Frontend deployment?
Azure Web Apps, Azure Front Door, and DevOps pipelines make it easy to host, scale, and manage Micro-Frontend architectures efficiently.
4. Are Micro-Frontends suitable for all applications?
They’re ideal for large enterprise applications but may add unnecessary complexity for small projects.
5. How do Micro-Frontends improve DevOps workflows?
They allow independent deployments, reducing release friction and enabling continuous integration and delivery.







Write a comment ...